Promoting Article 6 cooperation and engagement
The Article 6 page offers a comprehensive overview of Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, and subsequently outlines the process from developing a national strategy to the international transfer of mitigation outcomes. It features three dedicated subpages with resources to support countries in engaging effectively with Article 6. These sections address key strategic questions related to participation, national implementation needs, and the evaluation of activities and approaches. By selecting the dropdown menus, you can access the necessary guidance and materials for pursuing this cooperative journey, with the aim of amplifying impact and ensuring that the benefits of carbon market participation are shared and distributed fairly.
What is Article 6 of the Paris Agreement?
Market-based cooperation, enabled by Article 6 of the Paris Agreement plays an important role to channel funds for the implementation of climate mitigation to achieve Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and raise mitigation ambition.
Article 6 establishes guidance for reporting, accounting, and tracking of international market-based cooperation (Article 6.2), as well as a successor to the CDM, the Paris Agreement Crediting Mechanism (PACM) or Article 6.4 Mechanism. Furthermore, it puts in place a framework for non-market based approaches (Article 6.8). The information note dives deeper into the key components of Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, while emphasising the critical importance of developing a robust project pipeline and advocating for upfront finance.
Download Information Note on Introduction to Article 6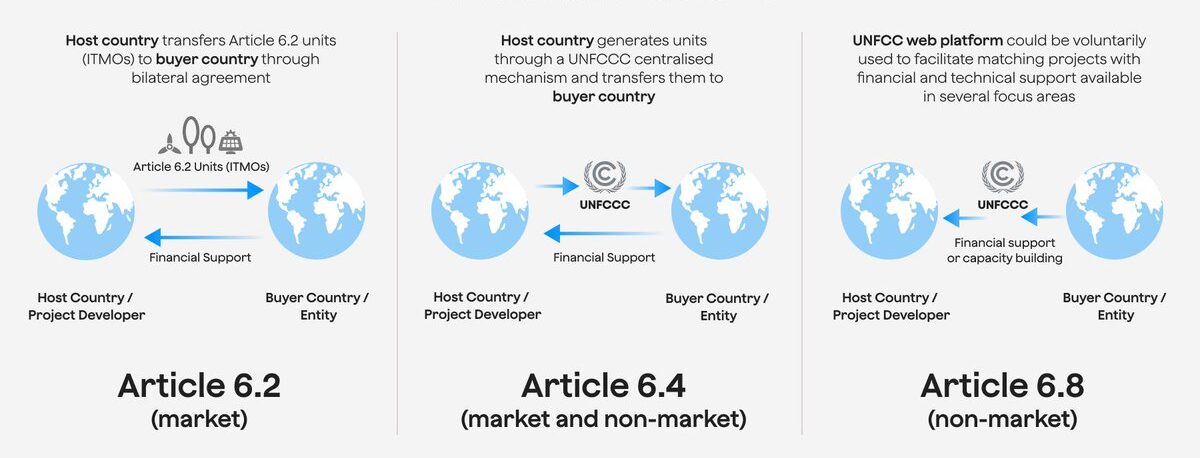
Guide: Pocket Guide to Article 6 (ECBI & PCG 2022)
Capacity Building Course: Article 6.2 operationalization (UNDP 2023) in English, Spanish, French
Explainer: Article 6 Explainer [updated with COP30 decisions] (The Nature Concervancy 2025)
Checklist: Tips for identifying non-market based approaches (UNFCCC 2025)
How to engage strategically?
Engaging in Article 6 requires strategic decisions about how to incorporate carbon markets into national climate governance structures and policies, how to comply with international reporting requirements and how to define what goals a country wants to achieve by using Article 6. Consequently, understanding the national starting point is an fundamental intial step when engaging in Article 6. Active Article 6 participation depends on close collaboration with project developers, international partners, including buyers and providers of technical assistance, as well as other relevant stakeholders to establish a strong pipeline of activities in the country.
Explore Article 6 Strategic Engagement
What is needed for national implementation?
Engaging with Article 6 requires the establishment of robust frameworks and processes, including procedures for authorisation, activity registration, accounting of mitigation outcomes, and reporting. Countries can build upon existing structures, refining them to align with national priorities and circumstances, while ensuring full compliance with Article 6 requirements.
Explore Article 6 Implementation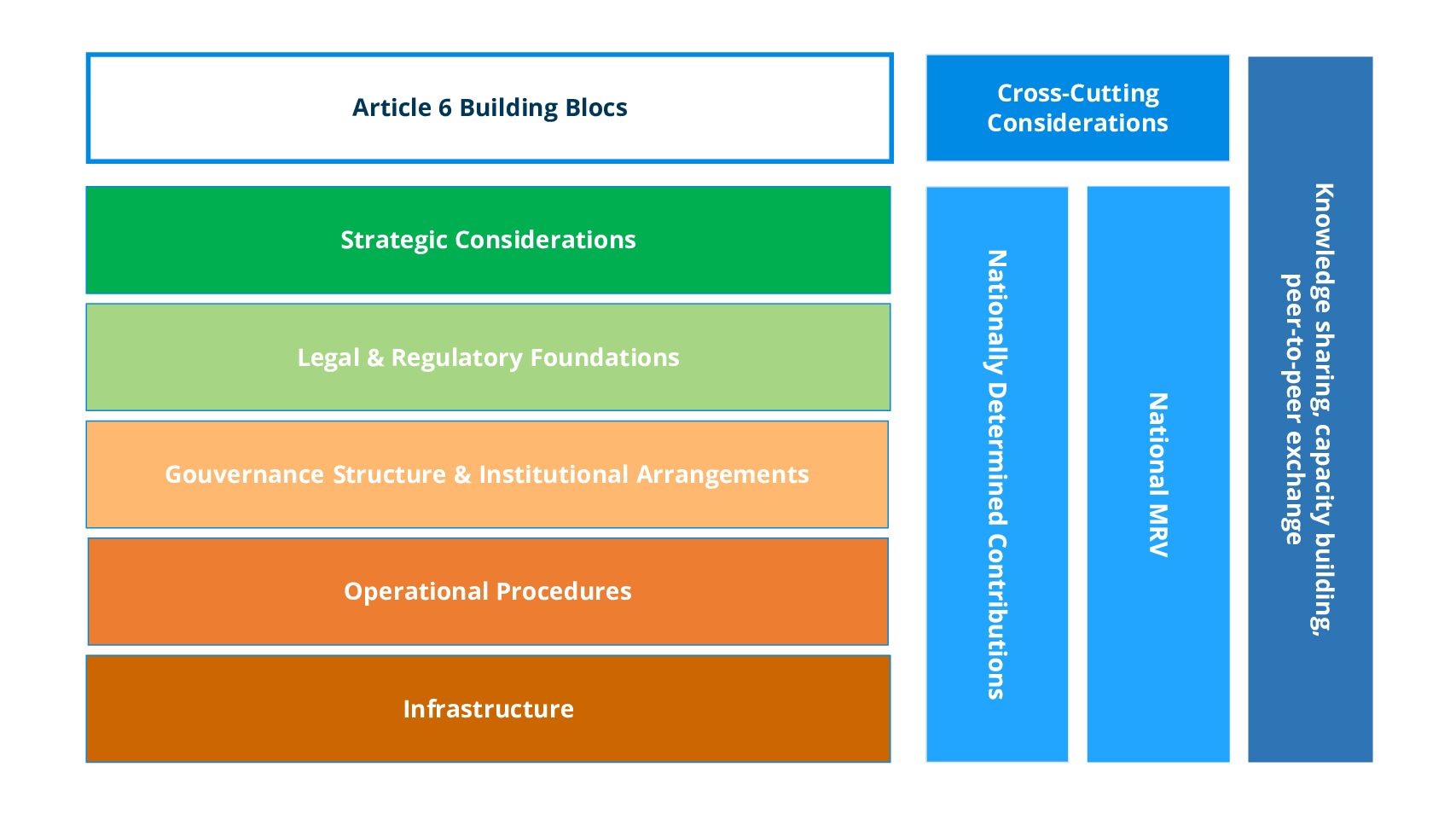
How to assess activities and cooperative approaches?
Many West African countries have progressed towards Article 6 readiness in recent years by developing regulatory frameworks and institutional structures for carbon markets. Now that the international rules for Article 6 have been agreed, countries can seize opportunities to advance and foster the development of high-integrity carbon market activities. This page points to different approaches, through which impactful projects can be identified and developed over time. It provides orientation to ensure alignment of activities with national climate targets, provides insights on contractual structures and relevant links to make well-informed decisions regarding credit pricing.
Explore Article 6 Activity Assessment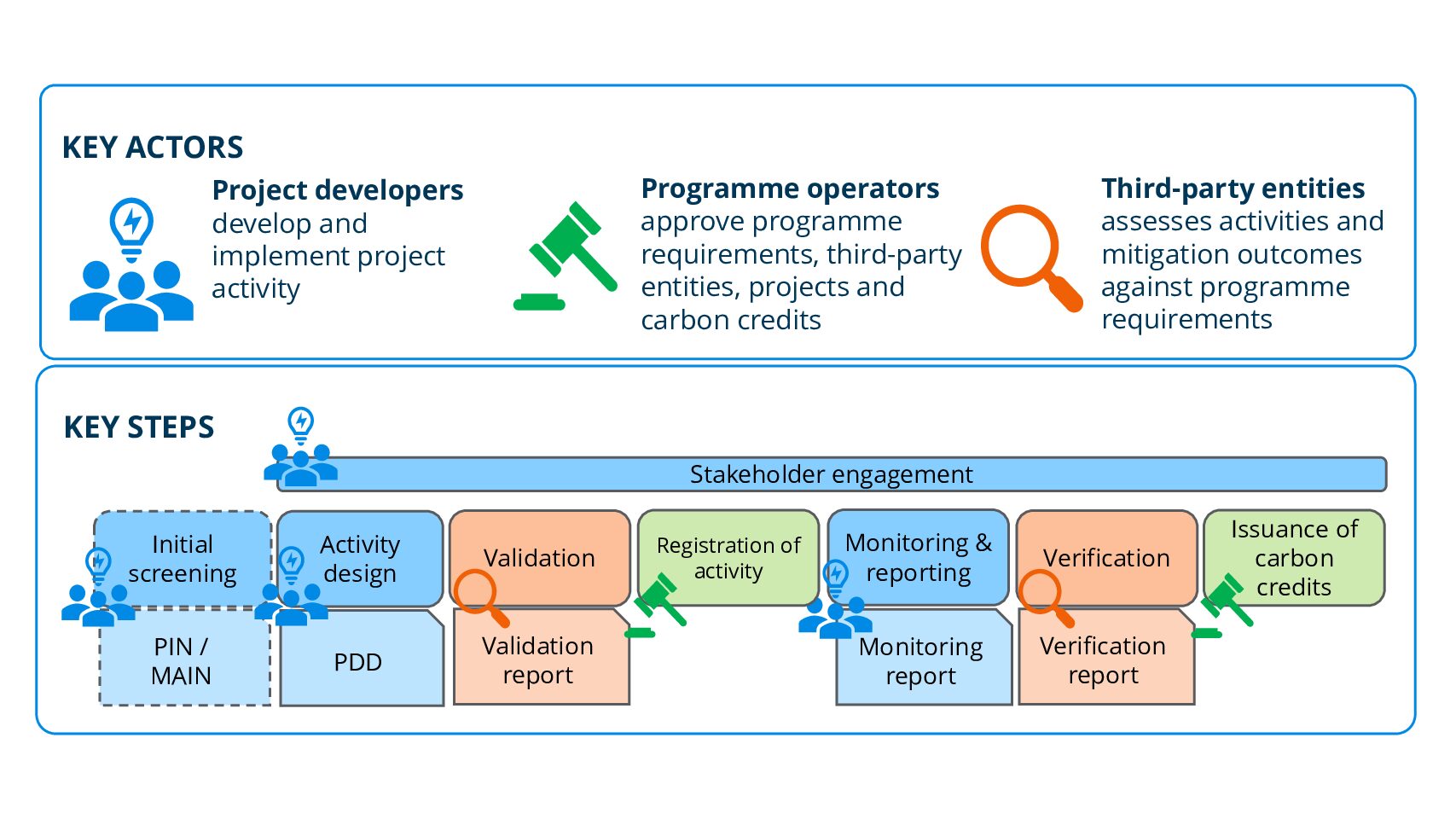
Understanding the numerous acronyms and terminology
Navigating the international carbon market landscape can be challenging due to the numerous acronyms and terms in use. These terms arise from the complex array of agreements, institutions, and frameworks that play a role in global climate mitigation efforts. This acronym-rich environment requires stakeholders to become familiar with a wide range of terminology, reflecting the intricate and multifaceted nature of international climate action. By clicking the buttons below, you will find a list of common acronyms used and a glossary of key terms.
Download Article 6 Acronyms List
Comprehensive resources on Article 6
- Database: Article 6 Pipeline (UNEP-CCC 2026)
- Report: The Paris Agreement Article 6 Implementation Status Report (AI6P 2025)
- Explainer: Article 6 Explainer [updated with COP30 decisions] (The Nature Concervancy 2025)
- Toolkit: High-Integrity Carbon Markets Toolkit (UNDP 2025)
- Report: The landscape of Article 6 implementation (PCG & CF 2023)
Click here to explore our Individual Member Country pages, where you can find information on west african national carbon market strategies, frameworks for Article 6 transactions, and additional insights
